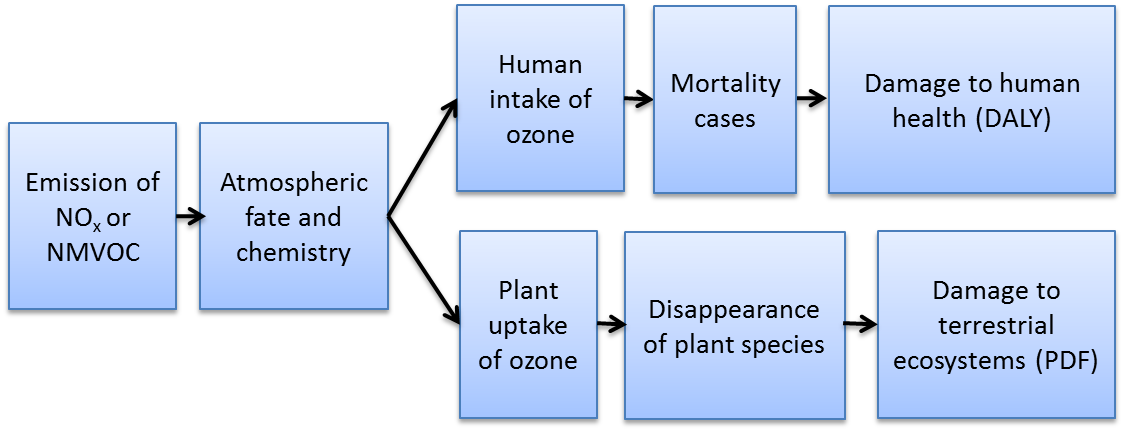
Air pollution causing tropospheric ozone in the atmosphere can have a negative impact on human health, e.g. respiratory problems, and terrestrial ecosystems, e.g. plant biomass decrease.
Cause-effect pathway
The impact model is addressing emissions of nitrogen oxides (NOx), and non-methane volatile organic compounds (NMVOC) and consequent effects on the Areas of protection ‘Human Health’ and ‘Terrestrial ecosystems’. This overview will focus on the human health effects only.
Modeling approach
A marginal approach for calculating the characterization factors is followed, meaning that the additional impact of a marginal increase in ozone precursor emission using today’s situation as the reference state was determined. Model results were determined following a change in anthropogenic emissions and is determined by lowering the year 2000 emissions by 20% for each of the 56 source regions. Impact is measured in disability adjusted life years for human health (DALYs) for human health.

