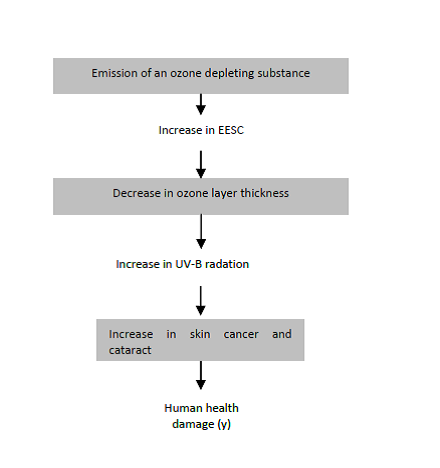
The stratospheric ozone layer blocks a large part of the harmful UV radiation before it reaches the surface. Certain (mostly bromine and chlorine containing) substances however have the potential to destroy stratospheric ozone and thereby increase the amount of radiation that reaches the surface which causes damage to ‘Human Health’.
Cause-effect pathway
After emission to air ozone depleting substances (ODS) spread throughout the atmosphere and eventually they will end up in the stratosphere where their chlorine and bromine groups interact with and destroy the ozone.
Modeling approach
A marginal approach is used to calculate the effect factors. Semi-empirical data (based on well recorded historic emissions of ozone depleting substance) is used to determine the effect of the different substances on the EESC (Equivalent Effective Stratospheric Chlorine). The EESC is a measure for how much stratospheric ozone can be destroyed. By calculating the resulting (optical) ozone layer thickness the amount of radiation that reaches the earth can be estimated. The increase in skin cancer (and cataract) can be determined from the amount of radiation, however this is dependent on the amount of skin pigment the population has (more pigment means less chance of getting skin cancer). Whether or not exposure to UV radiation causes cataract is uncertain.

