"Water for food is one of the main global issues and irrigation is a limiting factor in agricultural production. Food supply is a vital human need and insufficient nutrition accounts for ~ 3% of overall global health impacts (WHO 2014) and further contributes to impacts form other diseases. While many factors contribute to this issue, reduced water availability caused by water consumption leads to reduced availability for food production and consequent yield losses.
Cause-effect pathway
The impact model is addressing lack of water for agricultural food production and consequent effects on the Area of protection ‘Human Health ’ caused by water consumption.
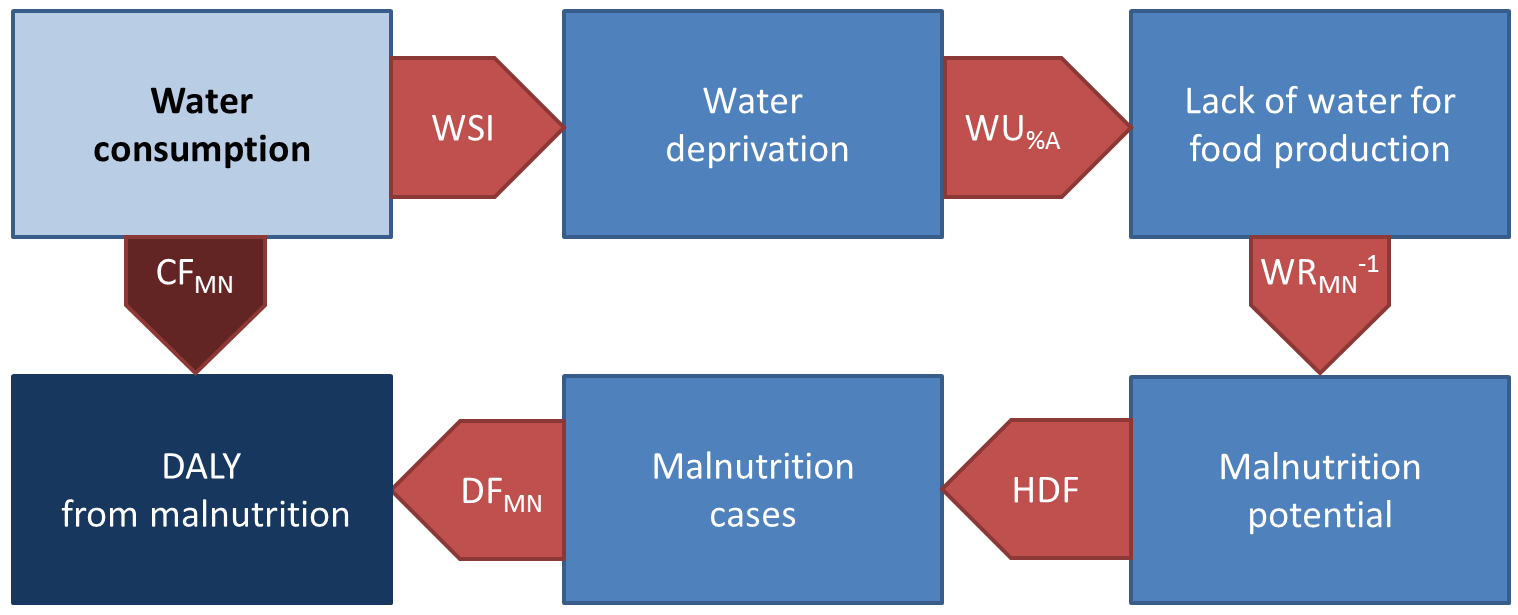
Modeling approach
Two different methods are available: (1) marginal CFs, which are typically used in LCA to address impacts of additional water consumption (marginal change in water consumption rate) and (2) average CFs, which are used to assess total impacts of water consumption within a region and to characterize the impact of an activity proportionally to the impact of total water consumption.
Value choices
A number of choices have been made for the calculation of the characterization factors, namely:
- Time Horizon:The time horizon is infinite, assuming steady-state conditions. The effect of water consumption is described through competition for a renewable resource on annual level.

